EPJ Data Science Highlight - Behavioural studies from mobile crowd-sensing
- Details
- Published on 18 December 2015
Smart phone monitoring has become a boon for scientists studying human behaviour and factors influencing stress
Using mobile phones for research is not new. However, interpreting the data collected from volunteers’ own smart phones--which has the potential to emulate randomised trials--can advance research into human behaviour. In a new study published in EPJ Data Science, scientists have just demonstrated the potential of using smart phones for conducting large-scale behavioural studies.The results stem from the work of Fani Tsapeli from the University of Birmingham, UK, and her colleague and Mirco Musolesi from University College London, UK. In their study, they evaluate the cause of increased stress levels of participants using user-generated data, harvested from their phones.
Most of the research work relying on smart phones has focused on detecting factors in the features extracted from smartphone data. The trouble is that pure correlation analysis does not provide for a sufficient understanding of human behaviour. Instead, scientists are now increasingly interested in identifying factors that could be at the root cause of issues revolving around health and well-being.
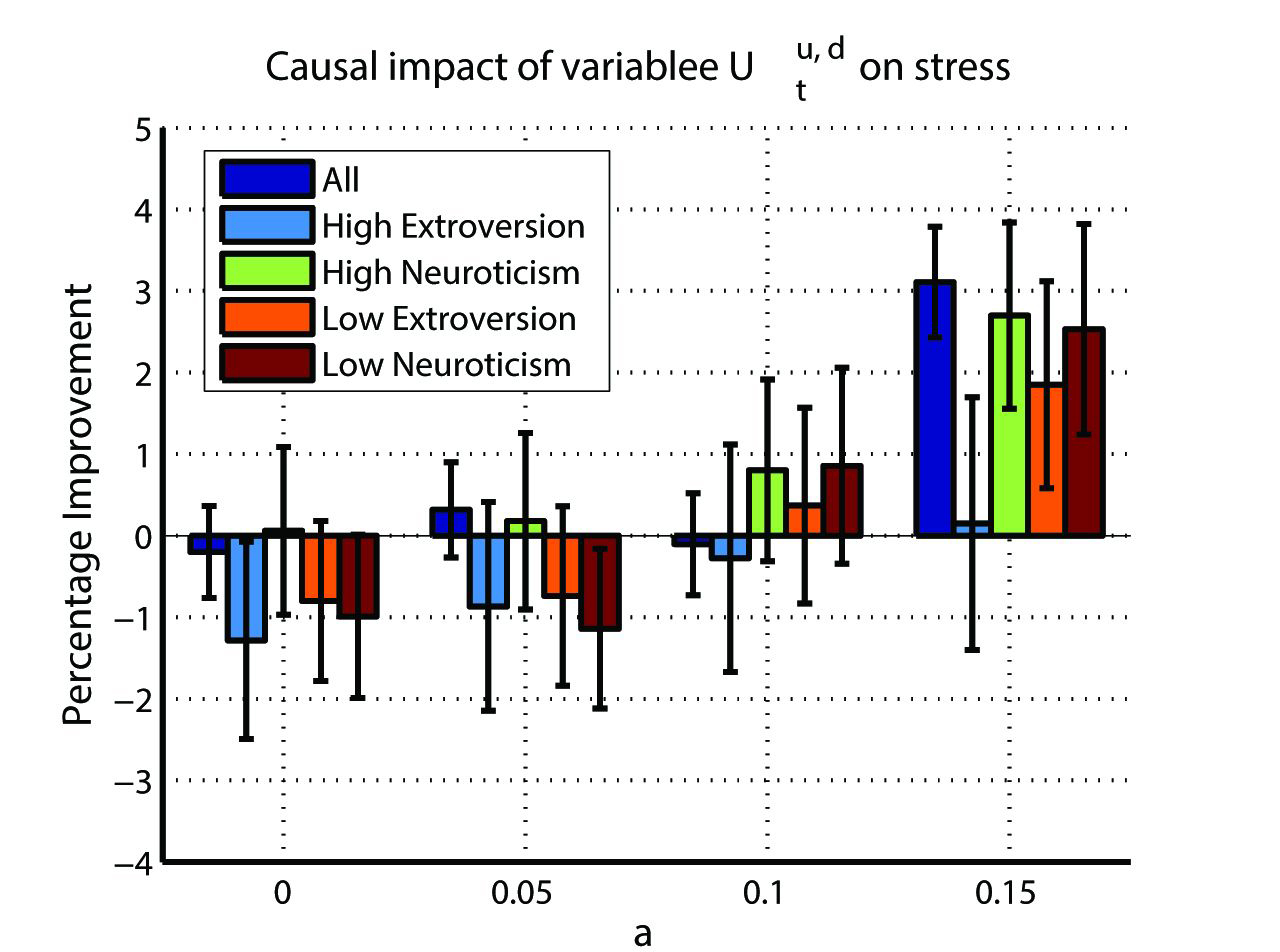
In this study, the authors used data from a research project at Dartmouth College, Hanover, USA, called StudentLife. It includes information on participants’ location taken from raw GPS data, which helps determine whether they are working or socialising. Also included is data on activity levels, like running, walking or travelling on public transport, inferred from participants’ raw accelerometer data.
They found that exercising and spending time outside the home and working environment have a positive effect on participants’ stress levels. By contrast, they found that reduced working hours only slightly impact stress. The conclusions cannot be extended to the general population due to the small sample size. But the approach has been validated and shows great promise for further studies.
F. Tsapeli and M. Musolesi (2015), Investigating causality in human behaviour from smartphone sensor data: a quasi-experimental approach, EPJ Data Science, 4:24, DOI 10.1140/epjds/s13688-015-0061-1





