EPJ A Highlight - An overview of the management structure of the AGATA collaboration
- Details
- Published on 25 September 2023
The AGATA project could eventually lead to a deeper understanding of the strong nuclear force. This paper details the project’s highly sophisticated management structure, which will be essential to achieving this goal.
The Advanced Gamma Tracking Array (AGATA) is a European gamma-ray spectrometer that is already achieving unparalleled levels of sensitivity in nuclear gamma-ray spectroscopy. Ensuring success in the project’s construction and operation has involved developing a highly sophisticated structure of management and organisation. This contribution to the EPJ A topical collection “AGATA: Advancements in Science and Technology” describes the roles and responsibilities of each of AGATA’s management committees, and details the project’s scientific organisation. As AGATA promises to make major breakthroughs in our understanding of the strong nuclear force and nuclear structure in the coming decades, the paper offers a new degree of transparency for the many research groups which stand to benefit from its future discoveries.
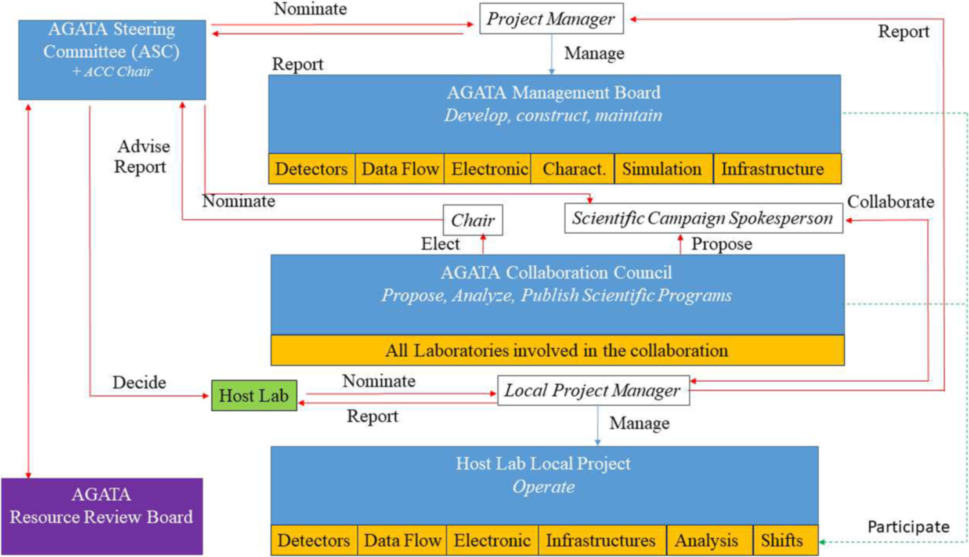
Eventually, AGATA will be able to track the trajectories and origins of gamma rays produced by nuclei created by intense, stable beams of rare radioactive isotopes. To achieve this, its future design will feature 180 segmented detectors made from high-purity germanium, arranged in a spherical structure. Since 2010, the project has been hosted by several different major facilities in Europe, and has seen its number of detectors steadily increase. Such deeply complex logistics required AGATA to constantly adapt to new instrumentations and to exploit efficiently the local infrastructures coupled to it – which has now led to a comprehensive, efficient management structure, encompassing all of its scientific, technological, and financial aspects.
AGATA is governed by a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), which guides crucial aspects of the project including its planning, funding, construction, and operation. It also specifies an overarching management structure which aims to maximise the breadth and quality of its scientific output at each facility. The latest MoU was signed in 2021 by 11 different countries, involving 38 institutions. In this paper, the four main committees of the MoU’s management structure and their relationships are explained in detail. Their main aim is to realize the best experiments to unveil the still unknown nuclear structure properties.
Clément, E., Bracco, A., Gadea, A. et al. Organisation of the AGATA collaboration and physics campaigns. Eur. Phys. J. A (2018) 59: 152 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-023-01057-w




