EPJ B Highlight - Better mastery of heat flow leads to next-generation thermal cloaks
- Details
- Published on 22 November 2017
Chinese physicists manipulate the transfer of thermal energy as a means of reducing heat waste, using thermal camouflage tactics
Ever heard of the invisibility cloak? It manipulates how light travels along the cloak to conceal an object placed behind it. Similarly, the thermal cloak is designed to hide heated objects from infrared detectors without distorting the temperature outside the cloak. Materials for such cloaks would need to offer zero thermal conductivity to help camouflage the heat. Now, Liujun Xu and colleagues from Fudan University, Shanghai, China, have explored a new mechanism for designing such materials. These findings published in EPJ B could have implications for manipulating the transfer of thermal energy as a way to ultimately reduce heat waste from fossil fuels and help mitigate energy crises.
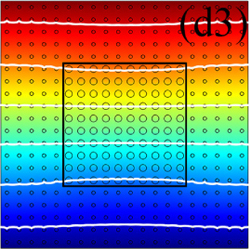
In this work, for the first time the authors experimentally verify that the inner composition of materials, which presents a non-uniform periodic structure, can exhibit quasi-uniform heat conduction. To do so, they use an infrared camera to detect heat in experimental samples placed between a hot and cold bath. These results confirm their own equations predicting the thermal conductivity of the periodic material.
To achieve the desired thermal illusion, they rely on quasi-uniform heat conduction. Instead of producing an omnidirectional illusion, showing objects with the same temperature signature regardless of the angle of observation, the authors introduce what they refer to as the Janus thermal illusion. It features an object whose heat is not detectable from one direction, thus forming an invisible illusion. By contrast, it features a different heat signature than its actual signature along the vertical axis, thus forming a different type of illusion, which is visible but not displaying the reality.
To remove the influence of thermal convection and radiation from their experimental results, the authors also perform simulations. These in turn help to develop the concept of ‘illusion thermal diodes’, which approach thermal illusion as an additional degree of freedom for heat management. Ultimately, these diodes could be applied in fields that require both thermal camouflage and thermal rectification.
L. Xu, C. Jiang, J. Shang, R. Wang and J. Huang (2017), Periodic composites: Quasi-uniform heat conduction, Janus thermal illusion, and illusion thermal diodes,
European Physical Journal B 90: 221, DOI: 10.1140/epjb/e2017-80524-6





