EPJ B - Quantum information motion control is now improved
- Details
- Published on 10 August 2012
Model simulates closer control over the transport of information-carrying electrons.
Physicists have recently devised a new method for handling the effect of the interplay between vibrations and electrons on electronic transport. Their paper has been published in EPJB. This study, led by scientists from Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, and the Centre for Computational Science and Engineering at the National University of Singapore, could have implications for quantum computers due to improvements in the transport of discrete amounts of information, known as qubits, that are encoded in electrons.
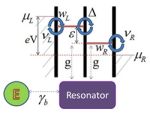
The authors created an electron transport model to assess electrons’ current fluctuations when they are subjected to quantized modes of vibration, also known as phonons. In the model, phonons are induced by a nanomechanical resonator. To better monitor electron transport, it is coupled to a system that was chosen for its ability to confine one or several electrons, called double quantum dot (DQD). Unlike previous studies, this work imposed arbitrary strong coupling regimes between electrons in the DQD and the phonons produced by the resonator.
The authors successfully controlled the excitations of the phonons without impacting the transport of quantum information. To do so, they decoupled the electron-phonon interaction by the so-called coherent phonon states method, which is based on reaching resonance modes of phonons. They have shown that when the energy excess between the two quantum dots of the DQD system is sufficient to create an integer number of phonons, electrons can reach resonance and tunnel from one quantum dot to the other. In strong electron-phonon coupling regimes, multi-phonon excitations can thus enhance the electron transport.
As the electron-phonon coupling becomes even stronger, the phenomenon of phonon scattering represses electron transport and confines the electrons. The fluctuations of electron current could therefore be controlled by tuning the electron-phonon coupling, which makes it a good quantum switch to control the transport of information in quantum computers.
Quantum transport of double quantum dots coupled to an oscillator in arbitrary strong coupling regime
C. Wang, J. Ren , B. Li, Q-H. Chen, Eur. Phys. J. B (2012) 85: 110, DOI: 10.1140/epjb/e2012-30027-1




