EPJ B Highlight - Novel materials: smart and magnetic
- Details
- Published on 10 February 2013
Varying magnetic fields and temperature conditions help to elucidate smart materials’ transitory magnetic disorder
Novel, smart materials like shape memory alloys very often display so-called glass-like magnetism. Other smart materials with similar properties include those which, when exposed to a magnetic field, change their electrical resistance, known as manganites, or change their temperature, known as magnetocaloric materials. Kaustav Mukherjee and his colleagues from the Consortium for Scientific Research Indore in India studied a key stage in the formation of such a magnetic glass material, called Pr0.5 Ca0.5 Mn0.975 Al0.025 O3, in a paper just published in EPJ B.
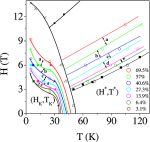
They focused on the stage where ‘water to ice’ style transformation—referred to as first-order magnetic transformation— is arrested upon cooling. This is a phenomenon dubbed kinetic arrest, corresponding to a temperature where the material undergoes a transition from a magnetic to a non-magnetic state, with the two phases competing with each other.
Glass-like magnetic materials display fragile magnetic properties. They draw their name from the similarity to the fragility observed in conventional, chemical glass. If a magnetic field is applied while the sample is cooled to what is referred to as its transition temperature, magnetisation of the sample increases and the material becomes magnetic. However, the magnetisation continues to increase further with time, even if the magnetic field and temperature remain constant.
The authors performed bulk measurements of magnetisation on powder samples of Pr0.5 Ca0.5 Mn0.975 Al0.025 O3, at the transition point between magnetic and non-magnetic states. To do so, they simultaneously varied both the magnetic field and the temperature of the sample. They observed the formation of the kinetic arrest band and showed that it is inversely correlated with states reached at extremes of temperature described at supercooling and superheating bands. They then established that the kinetic arrested state is different from the supercooled state.On the correlation between supercooling, superheating and kinetic arrest in a magnetic glass Pr0.5 Ca0.5 Mn0.975 Al0.025 O3. K. Mukherjee, Kranti Kumar, A. Banerjee and P. Chaddah (2013), European Physical Journal B 86: 21, DOI: 10.1140/epjb/e2012-30748-y




