EPJ E - How to build doughnuts with Lego blocks
- Details
- Published on 10 August 2012
Controlling forces between oppositely charged polymers opens a new route towards creating vectors for gene therapy
Scientists have uncovered how nature minimises energy costs in rings of liquids with an internal nanostructure made of two chemically discordant polymers joined with strong bonds, or di-blocks, deposited on a silicon surface, in an article published in EPJE.
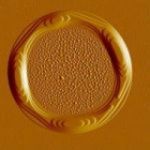
Josh McGraw and his colleagues from McMaster University, Canada, and the University of Reading, UK, first created rings of di-block polymers that they liken to building doughnuts from Lego blocks due to the nature of the material used. This material has an internal structure discretised like Lego blocks, resulting in rings approximating the seamless shape of a doughnut (see photo of previously unseen nanoscale assemblies which illustrates this press release).
McGraw and his colleagues measured the dynamics of interacting edges in ring structures that display asymmetric steps, i.e., different spacing inside and outside the ring, when initially created. They found that the interaction shaping the ring over time is the repulsion between edges. While the molecular details remain elusive, the source of this repulsion is intuitive: an edge is a defect which perturbs the surface profile with an associated cost to the surface energy.
The edge repulsion prevents two neighbouring edges from getting too near each other. As two isolated edges approach, the perturbation deviates further, thereby deforming the equilibrium edge structure and increasing the free energy. For rings solely subject to the repulsive edge interaction, the authors found that the equilibrium shape of their edges had to be symmetric.
These edges could be considered defects in a material with an otherwise perfect order at the nanoscale. Thus, research based on the elucidation of defect interactions could help scientists trying to eliminate such defects by understanding how these materials self-assemble. Such systems could also provide an ideal basis for creating patterns on the nanoscale, data storage, and nanoelectronics.
Dynamics of interacting edge defects in copolymer lamellae.
J.D. McGraw, I.D.W. Rowe, M.W. Matsen, and K. Dalnoki-Veress, Eur. Phys. J. E (2011) 34: 131, DOI 10.1140/epje/i2011-11131-7




