EPJ E Highlight - Horizontal levitation: the ultimate solution to particle separation
- Details
- Published on 07 June 2014
Separating particles from the liquid they are in can now be done with a new concept, based on horizontal deflection during particle levitation for the separation of minerals and particles.
Magnetic separators exploit the difference in magnetic properties between minerals, for example when separating magnetite from quartz. But this exercise becomes considerably more complex when the particles are not magnetic. In the wake of previous particle levitation experiments under high-power magnetic fields, a new study reveals that particles are deflected away from the magnet’s round-shaped bore centre in a horizontal direction. Previous studies had observed the vertical levitation of the particles. These findings are presented by Shixiao Liu from the Faculty of Engineering, University of Nottingham, UK and colleagues, in a paper recently published in EPJ E, and could led to a new concept in particles and minerals separation technologies.
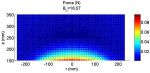
The authors analysed video frames covering 0.1 second each of the movement of glass and pyrite particles of roughly 1 millimetre diameter in a solution that were subjected to a strong non-uniform magnetic field created by a superconducting magnet. The authors show that pyrite and glass particles were deflected and settled at certain positions in a specially designed container. They explain that this pattern is due to differences in the particles’ densities and magnetic susceptibilities.
The gradient in the magnetic field gives rise to a radial force—defined by the particle’s magnetic properties—capable of separating the glass from pyrite particles. At the same time, the magnetic field gradient also induces the so-called Magneto-Archimedes force, which compensates for the force of gravity. Surprisingly, the particle size seems to have little influence on the results, at least for the limited size range examined in these experiments.
The authors then confirmed their experimental findings using mathematical simulations of the particle displacement.
Horizontal deflection of single particle in a paramagnetic fluid. S. Liu, Xiang Yi, M. Leaper, N.J. Miles (2014), Eur. Phys. J. E, DOI 10.1140/epje/i2014-14047-8





