EPJ D Highlight - Novel beams made of twisted atoms
- Details
- Published on 01 August 2013
Scientists can now theoretically construct atomic beams of a particular kind, opening the door for applications in fields like quantum communication.
Physicists have, for the first time, now built a theoretical construct of beams made of twisted atoms. These findings are about to be published in EPJ D by Armen Hayrapetyan and colleagues at Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg in Germany. These so-called atomic Bessel beams can, in principle, have potential applications in quantum communication as well as in atomic and nuclear processes.
The concept for twisted atom beams stems from a similar approach with twisted photon beams, which are currently used as optical tweezers, for instance. It was later extended to twisted electron beams, which are used to improve the magnetic mapping of biological specimens and magnetic materials by means of twisted electron microscopy.
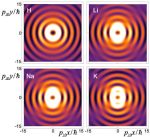
The authors focused on a beam made of twisted two-level atoms, which are driven by a laser field. They created a theoretical construct by using an equation, referred to as the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation, for atoms which are moving much slower than the speed of light. Hayrapetyan and colleagues solved this equation by taking into account the propagation directions of both the atomic and laser beams. By superimposing a multitude of plane waves with well-defined amplitudes, they produced Bessel beams for two-level atoms that resonantly interact with the laser field.
The authors confirmed that their atomic beams fulfilled the two main characteristics of Bessel beams. First, they showed that these beams carry a non-zero orbital angular momentum, as reflected by a rotation of the beam’s wave front around the propagation axis in a corkscrew-like manner. Second, by taking a snapshot of the atomic beam intensity they demonstrated that these beams do not spread along the propagation axis. Moreover, they were able to control the profile of laser-driven atomic Bessel beams by tuning the parameters of both the atomic and laser beams.
Bessel beams of two-level atoms driven by a linearly polarized laser field, A.G. Hayrapetyan, O. Matula, A. Surzhykov and S. Fritzsche (2013), European Physical Journal D, DOI 10.1140/epjd/e2013-30191-x




